When it comes to marketing strategy, it is essential to understand the forces that shape the industry in which a company operates. One of the most commonly used methods for assessing the competitiveness of a sector is Porter’s 5 Forces analysis.
💡 This approach, developed by Professor Michael E. Porter of Harvard University, is designed to help companies understand competitive dynamics and develop appropriate strategies to stand out in the marketplace, and thus ensure the long-term survival of their business, as well as making important strategic decisions. 💰
- 😱 But is this technique, which dates back to 1979, still relevant today?
- 😨 Wouldn’t it be better to review or rethink the system?
Let’s take a closer look at what it looks like and how to adapt it.
What are Porter’s 5 forces?
Porter’s 5 Forces marketing analysis involves assessing five key factors that determine an industry’s competitive intensity.
These forces include:
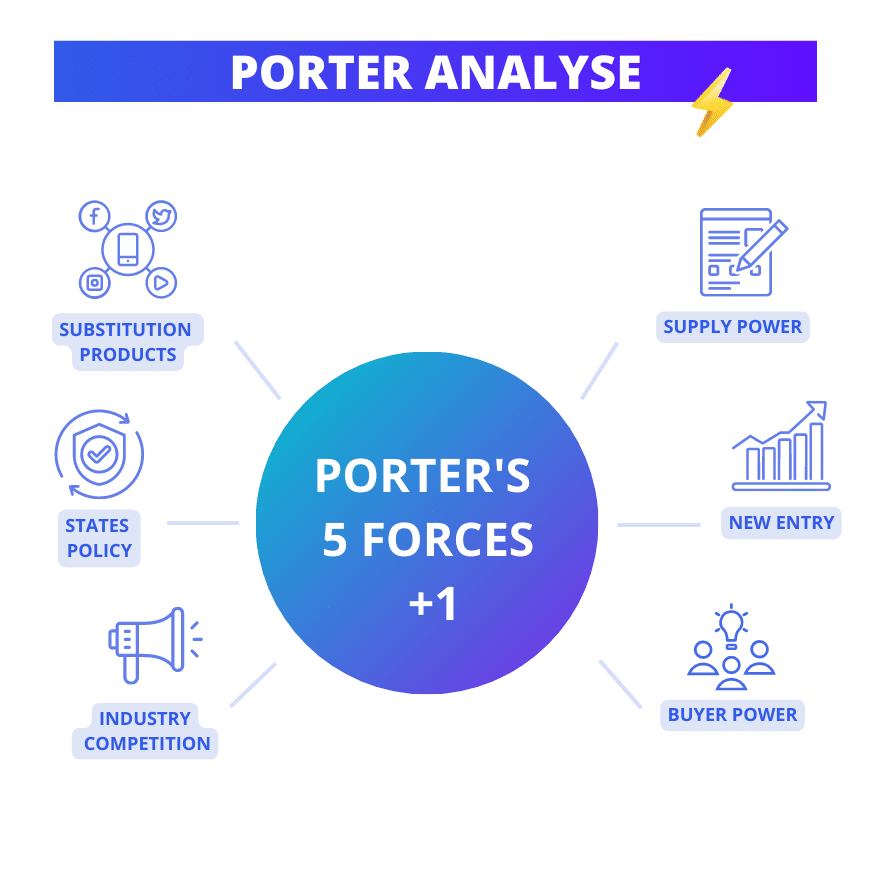
Supplier bargaining power
This is the ability of suppliers to influence prices, quality and supply conditions. The more powerful suppliers are, the more they can impose their demands on companies. For example, in the drinks’ industry, suppliers of raw materials such as sugar and packaging can exert influence.
The bargaining power of buyers
This is the ability of customers to influence companies in terms of price, quality and choice. If buyers have many options and can easily change suppliers, they have a high level of negotiating power. Take the fashion industry, for example, where consumers have a wide range of choices between different brands.
The threat of substitute products
This is the likelihood that customers will turn to alternatives to a company’s products or services. The more substitutes there are and the more attractive they are, the greater the competitive pressure. For example, in the drinks’ industry, energy drinks can be seen as potential substitutes for traditional soft drinks.
The threat of new entrants
This is the ease with which new companies can enter the market and compete with existing players. If barriers to entry are low, new entrants can upset the competitive balance. Take the fashion industry, for example, where new brands can easily emerge thanks to low-cost online sales channels.
The intensity of competition between market players
This is the rivalry between existing companies in the industry. If competition is fierce, companies have to fight to gain market share and maintain their competitive edge. The clothing industry, with brands such as Zara, H&M and Uniqlo, is an example of a sector where competition is particularly intense.
The role of government (5+1)
What role do public authorities play? Technical or even financial support to encourage deployment, integration into public policies, additional taxes, reduced charges, etc.
How do you carry out a Porter’s 5 forces analysis?
Today, we’re going to explore together the power of Porter’s 5 forces analysis 🚀 to assess the competitiveness of your business sector.
📈 This method will help you better understand the challenges you face and identify opportunities to stand out. Whether you’re in the digital sector, selling B2B services or selling B2C services, here’s how to carry out this analysis in a few key steps: 🗝️
1. Assess the threat of new entrants:
Take the time to consider how easy it is for new businesses to emerge and disrupt your market. 👀
Analyze the opportunities for new players and assess the threat they pose to your business.
🚧 Identify existing barriers to entry in your sector:
- In digital: barriers may be relatively low, allowing new start-ups to emerge.
- In the sale of B2B services: specialist knowledge and strong partnerships may constitute higher barriers.
- In the sale of B2C services: regulatory requirements and start-up costs can be significant barriers.
📊 Assess how easy it is for new players to enter your market:
- Identify opportunities for new entrants and assess their potential for disruption.
- Look for areas where you can strengthen your own barriers to entry to deter competition.
2. Supplier bargaining power
Analyze the bargaining power of your suppliers.
Identify the key suppliers in your sector and note them down on an Excel sheet, writing down the importance of each supplier.
👑 Evaluate their negotiating power by considering:
- The concentration of suppliers: are they numerous or rare?
- The availability of alternative sources of supply.
- The importance of their contribution to your supply chain.
▶️ Find actionable solutions:
- Diversify your sources of supply to reduce your dependence on a single supplier.
- Strengthen your relationships with key suppliers to gain advantages.
3. Your buyers’ bargaining power
Assess your customers’ bargaining power:
Identify the key customer segments in your sector and create personas.
👩🔬 Analyze their negotiating power, taking into account :
- Their persona,
- Their size and concentration.
- Their price sensitivity
- Their ability to look for alternatives.
🌞 Adopt practical solutions:
- Provide a unique value proposition to build customer loyalty.
- Boost customer satisfaction by offering excellent service and meeting their specific needs and pampering the UX. 💥
4. The threat of substitutes for your product
There are bound to be products or services they can buy instead of using yours. 👀
🔎 Identify potential substitute products or services in your sector:
- Look for alternatives that could meet customers’ needs in a similar or better way.
- Anticipate technological developments and consumer trends that could influence demand.
🎢 Find practical solutions:
- Constantly innovate to offer a unique value proposition that is difficult to replace.
- Monitor market changes closely and adapt quickly to new trends.
5. The intensity of competition between players in your market
Depending on the market, you may find yourself up against huge competitors who are already very well established.
🕵️ Analyze the level of competition in your sector:
- Identify your main competitors and assess their market position.
- Analyze their strengths and weaknesses, as well as their differentiation strategies.
📊 Adopt pragmatic actions:
- Highlight your competitive advantages.
- Constantly monitor your competitors and react quickly to market changes.
By following these steps, you will be able to carry out an in-depth analysis of Porter’s 5 forces in your sector of activity and develop concrete solutions to stay competitive.
What is Porter’s 6th strength?
In addition to the traditional five forces, some strategy experts have suggested adding a sixth force: the State. 👨👩👧👦
This force includes elements such as government regulations, social standards, environmental impact and ethical concerns. These factors can have a considerable influence on companies’ marketing strategies, particularly in response to the growing demand for sustainability and social responsibility.
Company examples and Porter’s 5 forces
Below, we take a brief look 🔍 at how Porter‘s 5 forces can be applied to three well-known companies: Coca-Cola, Danone and Zara.
Coca-Cola’s 5 Porter’s strengths:
| Porter’s strengths | Impact on Coca-Cola |
| Bargaining power of suppliers | Low, because Coca-Cola has close relationships with its suppliers and benefits from economies of scale, thanks to intense global production. 📈 |
| Bargaining power of buyers | Moderate, consumers have several choices of soft drinks and can easily switch brands, however “Coca-Cola “is a flagship product. |
| Threat of substitute products | Moderate, as there are other soft drinks and alternatives such as fruit juices, sodas 🥤 and energy drinks. |
| Threat from new entrants | Weak, Coca-Cola has colossal brand awareness, global distribution and huge financial resources! 👑 |
| Competitive intensity | High, Coca-Cola faces intense competition from other major beverage brands, both domestic and international. |
Danone’s 5 Porter’s strengths:
| Porter’s strengths | Impact on Danone |
| Bargaining power of suppliers | Moderate, Danone depends on raw material suppliers for its dairy products 🥛 and beverages. |
| Bargaining power of buyers | High, customers have several alternatives when it comes to dairy products and can be price sensitive, so if prices rise they will more easily go to competitors. 👀 |
| Threat of substitute products | Low, Danone offers specialized and essential products (water, milk). |
| Threat from new entrants | Low, Danone has ultra-high financial resources, know-how and partnerships 👐 which make it difficult for new players to enter. |
| Intensity of competition | Moderate, Danone faces competition from other major dairy brands, but retains a leading position, and the brand continues to buy many competing businesses to merge them 💰. |
Zara’s 5 Porter’s strengths:
| Porter’s strengths | Impact on Zara |
| Bargaining power of suppliers | Low, Zara maintains tight control over its supply chain. 👕 |
| Bargaining power of buyers | High, customers have a wide choice of brands and can easily compare prices and quality of clothing. (Pull and bear, H&M and many others). |
| Threat of substitute products | Low, clothing is a product that is difficult to substitute. 😆 Second hand could be a substitute product that can be taken into account and therefore, Vinted as the most competitive substitute brand. |
| Threat from new entrants | Moderate, the fashion industry is relatively accessible to new entrants, but Zara benefits from a fairly solid reputation. |
| Competitive intensity | High, there are countless other affordable fashion brands targeting similar segments. |
The 4 limitations of Porter’s 5 strengths (which spoil the whole analysis)
How can I tell you that you learn Porter’s 5 forces in your business studies, but today, there are many points to take into account in these analyses, and the technique should be largely revisited to the current trends… 😅

1. New forms of competition
Competition has changed considerably over the last ten years. 😨
Barriers to entry in many sectors have become less significant, because we discovered a magic tool called the internet that has shaped a new world, allowing new businesses and new business models to emerge. 🌍
Online platforms, innovative startups and data-driven businesses have disrupted traditional industries, Porter’s 5 categories don’t take technology advantages into account at all!
2. The importance of data and predictive analysis
Data plays a crucial role in strategic decision-making. Today we have data analysts and data scientists, and not for nothing. Data is the new key 🗝️ to do targeted marketing.
Companies that can collect, analyze and exploit data effectively can gain a significant competitive advantage! This goes far beyond Porter’s 5 forces analysis, because the emphasis is now on understanding trends, consumer behavior and opportunities through predictive analysis.
3. Rapid changes in the environment
The business environment is changing at a breakneck pace, with technological change, regulatory developments and consumer expectations constantly evolving. 🎢
Porter’s 5 forces, which are often based on a static analysis, may not fully capture changing dynamics. Companies need to be agile and able to adapt quickly to new market realities.
4. The importance of digital marketing and social networks
Digital has transformed the way companies interact with customers, manage their supply chain and develop partnerships. ▶️ Aspects such as online marketing, digital distribution, user experience and online reputation management are all dimensions that can boost a company’s competitiveness enormously… 💥
These points are rarely taken into account in the traditional Porter’s 5 forces analysis, but they should be.
FAQ on Porter’s 5 forces
Is Porter’s 5 forces matrix an internal or external analysis?
Porter’s 5 Forces matrix is an external analysis, as it examines the external factors that affect an industry’s competitiveness.
Who is Porter, and how did he come up with this matrix?
Michael E. Porter, a professor at Harvard Business School, is the author of Porter’s 5 Forces Matrix. He developed it in his 1980 book entitled “Strategic choices and Competition: techniques for analyzing industries and their competitors”.