Pricing strategies need careful consideration. 🧐 In fact, it’s a strategic decision that goes beyond profitability and directly affects the image, identity, and perception of the company’s offering… In this article, find the best pricing strategy examples of pricing policies you can use in your sales strategy. 🏹
What is a pricing strategy?
Pricing strategy is the pricing method used by companies, i.e., the set of decisions and actions taken to determine the selling price of goods and services. 🏷️
This decision is based on many factors. 👉 In particular, you need to consider the following:
- A company’s internal cost of maintaining profit margins and profitability,
- The cost “accepted” by the customer, i.e., the price they are willing to pay for the product or service,
- Competitors’ price positioning.
There are various pricing policies, the most common of which are: 👇
- Penetration pricing strategy,
- Skimming pricing strategy,
- Value-based pricing strategy,
- Competitive pricing strategy,
- Pricing strategy due to rising costs.
Here are the 10 examples of marketing pricing strategies we’re going to look at in more detail! ✨
10 Pricing Strategy Examples in Marketing
1. Low pricing strategy
The low price strategy is a technique used in marketing to attract consumers by offering lower prices than competitors. 👀
This approach aims to increase sales by offering affordable products and services, and is particularly effective for price-sensitive consumers. 👉 By lowering prices, companies can gain recognition and market share, generating more sales volumes.
However, this strategy can affect perceived product quality and may not be viable in the long term if profit margins are low. 🙈 Consequently, thorough market research and effective cost management are essential to the success of this strategy.
Example of a low-cost strategy:
Aldi, a German supermarket chain, is an example of a company using low-cost pricing. 💪 Founded in 1946, Aldi is known for offering quality products at very competitive prices.
The company follows a cost-cutting strategy by minimizing advertising, marketing, and inventory costs. 👉 This enables Aldi to offer products at prices below the market average.
This approach has enabled Aldi to establish itself as one of the leading food retailers in Europe and worldwide, 🌎 attracting a loyal, bargain-seeking customer base.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
|
2. High pricing strategy examples
The premium pricing strategy in marketing is an approach companies use to position their products and services as high-quality. 🤑
This method focuses on quality, innovation and exclusivity, and imposes higher prices than competitors. 👉 Such strategies aim to attract consumers willing to pay more for higher-quality products.
However, this can also lead to a drop in demand and require additional efforts to justify higher prices to customers. 😅
Example of a high price strategy:
When it comes to applying an expensive pricing technique, the prestigious French luxury brand Louis Vuitton clearly stands out from the competition. 👜
Since its creation in 1854, the fashion brand has always combined exclusivity, craftsmanship, and sophistication in its products. 🪶 With prices significantly higher than many other brands, Louis Vuitton not only positions its products as high quality, but also reinforces its premium brand image. 🪙
This strategy attracts customers who want to buy exclusive, high-quality items that demonstrate status and elegance. 👠
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
|
3. Penetration pricing strategy
In a competitive market, it can be difficult for new companies and products to establish themselves and gain market share. 🍰
Setting a lower price than your competitors can attract a wider potential customer base right from launch. 👉 This strategy is known as a penetration pricing policy.
It will help you attract customers and achieve valuable sales volume quickly. However, you need to guarantee your customers’ loyalty to maintain their interest even in the event of future price increases.
Example of penetration pricing:
Netflix is an example of a company that uses penetration pricing techniques. When Netflix launched its online video streaming service, it adopted an aggressive pricing strategy to differentiate itself from its competitors. 💥
They offered very low monthly subscription fees, encouraging consumers to try their service instead of traditional, expensive alternatives like cable TV. 😏
This strategy enabled Netflix to quickly build a loyal subscriber base, gain popularity and dominate the online video streaming market. 👉 Currently, they have raised their subscription prices and continue to gain new customers.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
|
4. Skimming pricing strategy examples
Price skimming, also known as skim pricing, is a pricing policy that sets higher prices for new products. 🚀
When a market becomes saturated, or when a product becomes obsolete and sales decline, a company may choose to lower the price of the product to attract a more price-sensitive market segment. 💲
Companies often resort to skimming prices when marketing innovative products with little competition. 👉 This strategy can also be used to target specific customer segments with high purchasing power.
Example of skimming prices: What pricing strategy does Nike use?
Major brands such as Nike provide excellent pricing strategy examples of skimming prices, known as “abusive”: 👇
Nike, a leader in the sportswear sector, regularly launches new models at high prices and relies on first-time buyers and loyal customers to purchase products at introductory prices. 💹 These prices are likely to remain in place for several months until Nike lowers the selling price of remaining stock for price-sensitive customers.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
|
5. Psychological pricing strategy
Psychological pricing techniques are pricing strategies that aim to make a product more attractive to consumers by setting a price slightly below the whole number. 🤔
For example, set the price at 9.99 euros instead of 10 euros. 💡 The difference is minimal, but it feels much cheaper. This approach takes advantage of human psychology.
In other words, consumers tend to focus on the leftmost number. 👈 By using this technique, companies aim to increase sales by giving the impression of a better deal.
It’s a powerful tool for influencing consumer perception and encouraging purchase. 👏
Example of psychological pricing:
H&M, an international fashion retail chain, is a good example of a company that uses psychological pricing techniques. 🧠 Browsing the shelves and their website, it’s not uncommon to find products priced at 19.99 euros or 49.95 euros.
This strategic approach gives customers the feeling that they’re getting a bargain, even if the discount is only a few cents. 🤑 The goal is to use price perception to stimulate purchase.
By combining this approach with regularly updated fashion trends, H&M has succeeded in attracting and retaining a customer base looking for style at an affordable price. 🧦
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
|
6. Promotional pricing strategy examples
Promotional pricing techniques are marketing strategies designed to attract consumers by offering temporary discounts on products or services. ⌚
This technique aims to create a sense of urgency and exclusivity for consumers and increase sales. 🧨 Promotional pricing can take many forms: discounts, coupons, free offers or flash sales.
These promotions can be integrated into advertising campaigns on a company’s website or in-store. 🏪 Promotional pricing techniques are particularly effective in encouraging customers to try new products or sell stock. 🥡
Example of promotional pricing:
Indeed, Zara, a well-known clothing brand in the fashion industry, 👘 uses promotional pricing techniques.
Zara regularly offers special deals, discounts, and promotions to attract customers and increase sales. 🚀 For example, Zara offers discounts of up to 50% on certain items during its summer sales.
What’s more, the brand also offers special deals for students with additional reductions on their purchases. 💣 These promotional pricing strategies are effective in attracting customers and boosting sales, while maintaining Zara’s business reputation.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
|
7. Differentiated price (added value)
A value-based pricing strategy determines the price of a product based on its perceived value to consumers. 😏 This strategy is particularly suited to products whose consumer-perceived value is significantly higher than the cost of production.
It is notably used in major brands and luxury products. 💎 It is also often used for products with highly differentiated characteristics or offering limited substitutes.
This pricing policy works well for social enterprises, as they can highlight the unique aspects of their business and manufacturing processes. ✍️ For some consumers, knowing that their purchase contributes to a social good justifies paying the extra cost of that product.
Example of pricing based on perceived value: What pricing strategy does Apple use?
Apple is an example of a company that uses value-based pricing techniques. By selling high-end products such as iPhones, iPads and Macs, Apple has created a perception of superior value for customers. 🤑
The brand skillfully communicates the unique benefits of its products, including innovative design, ease of use and high performance. 🚀
This gives Apple the opportunity to charge a higher price than other similar products on the market. 💲 Customers are willing to pay a higher price to benefit from a brand’s superior customer experience and superior quality.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
|
8. Dynamic pricing (Yield management)
Dynamic pricing is a pricing management strategy used by many companies to adjust prices in real time according to various factors such as demand, competition, production costs and customer preferences. ⚡
This approach enables companies to maximize profits by raising prices when demand is high and lowering them when demand is low. 🎢
Thanks to sophisticated data and algorithms, companies can analyze thousands of variables and make more accurate and profitable pricing decisions. 💰
Dynamic pricing techniques are increasingly popular in the e-commerce, travel services and hospitality industries, where prices often fluctuate according to supply and demand. ✈️
Example of dynamic pricing:
McDonald’s is an example of a company that uses promotional pricing techniques. 🍱 Fast-food chains often offer special deals on certain products, such as menu items or formulas.
For example, McDonald’s may offer its Big Mac menu at a reduced price for a certain period of time to entice customers to take advantage of exclusive offers. 🔥 This strategy enables the company to attract new customers while increasing sales of certain products.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
|
9. Bundle pricing strategy examples
Bundle pricing is a marketing strategy aimed at increasing product sales by offering consumers a package of related products or services sold at a total price lower than their individual prices. 😍
This approach aims to encourage customers to choose bundled offers to save money rather than buying each item individually. 💲
This can also help increase sales of less popular products by linking them to more attractive products. 😏 Bundle prices are often used to attract a wider customer base and grow the perceived value of the products on offer.
Example of bundle pricing:
An example of a company that uses bundle pricing techniques is Microsoft, which offers its Office 365 products. 💻 Rather than selling the various tools in its Office suite individually, Microsoft offers bundles of Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Outlook and many other applications as part of a monthly or annual subscription. 🌟
This strategy enables the company to generate recurring revenues from subscriptions while adding value for customers by bundling various software at attractive overall prices. 🪙
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
|
10. Market pricing strategy examples
The “market price” method is based on aligning the price of a product or service with a standard or average observed on the market. 🧐
This strategy requires careful study of competitors’ prices for similar products, rather than basing prices solely on production costs or perceived value. 🔍
Once this analysis has been carried out, the company will set a price slightly below, at the same level or above, depending on the desired positioning. 🎯
This approach enables companies to maintain a competitive edge while ensuring that their products remain etched in consumers’ minds. 💫
Example of a market pricing strategy:
Music streaming giant Spotify ably embodies the market pricing strategy. 🎼 By analyzing the monthly subscriptions of competitors such as Apple Music and Amazon Music, Spotify adjusts its prices to closely match current market prices, increasing consumers’ perception of subscription costs, thus avoiding major differences.
This strategy not only ensures competitiveness, but also keeps Spotify among the options that listeners consider economically viable. 💪
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
|
Conclusion: What are the 4 pricing strategies?
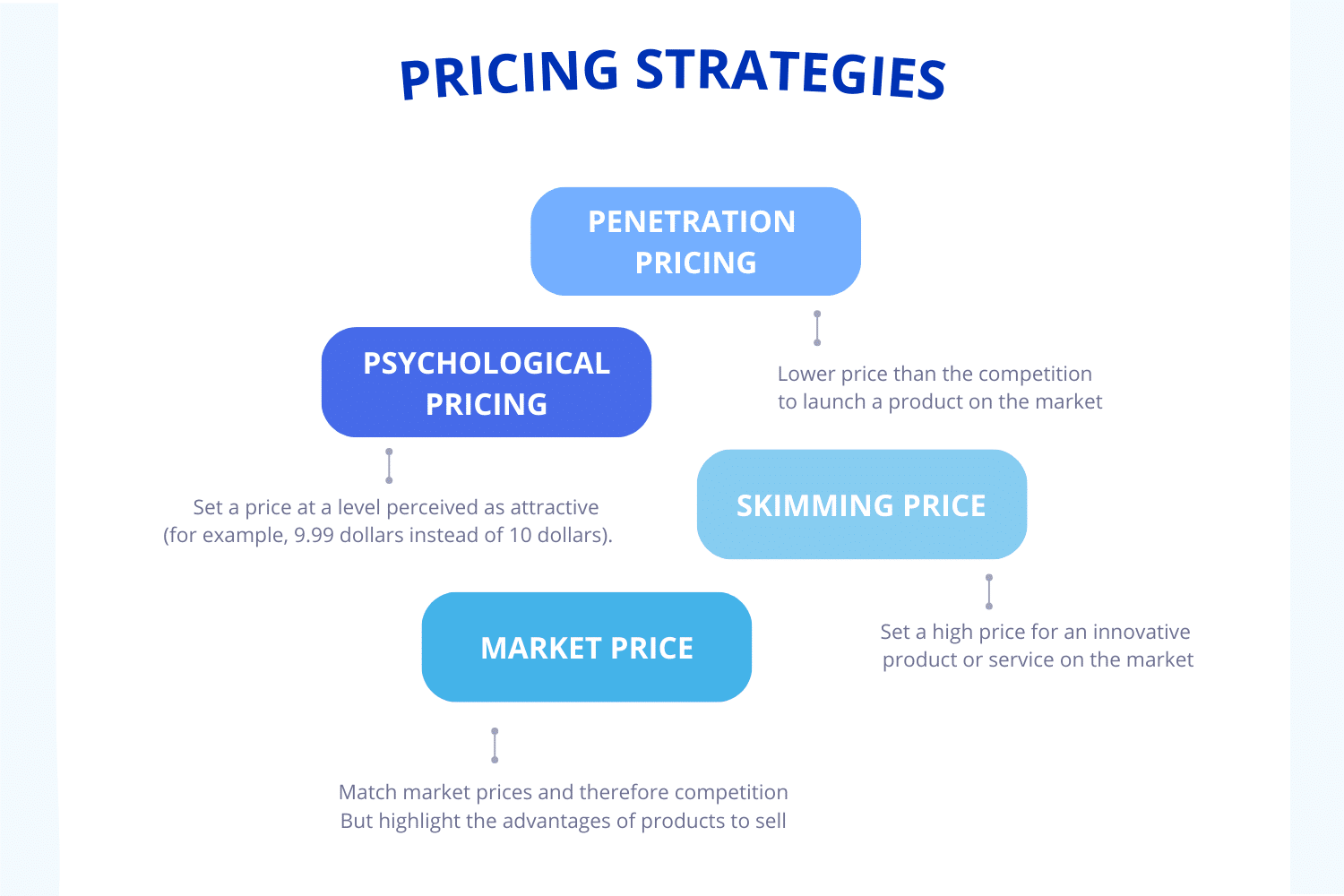
In conclusion, here’s a recap of the 4 main pricing strategies: ⏬
- Skimming price: set a high price for a new product, primarily targeting consumers willing to pay more.
- Penetration pricing: introduce new products at low prices to quickly attract customers and gain market share.
- Market price: align your product’s price with the market average or your competitors‘ prices.
- Psychological pricing: set the price at a level perceived as attractive (e.g., 9.99 euros instead of 10 euros).
Each strategy responds to specific objectives and market situations, so choose the one or ones that best suit your target. 🧲
Article FAQ: Pricing Strategy Examples
How to establish a pricing strategy?
Here’s how to create a pricing strategy in 5 steps: 👇
- Cost analysis: calculate all production and distribution costs and determine the break-even point.
- Market research: identify current demand, competition, and pricing trends.
- Define your USP: understand your unique selling proposition (USP) and how it differs from others.
- Choose a technique: skimming, intrusion, market pricing or a psychological approach.
- Continuous review: adjust your strategy regularly based on customer feedback and market trends.
An effective pricing strategy is essential for lasting success. 🤲 If you’d like to know about other selling price strategies then, follow this article!
What are the 4 Ps of marketing?
Here are the key pillars of the 4 Ps of marketing: 👇
- Product: this refers to the product or service on offer, its features, benefits, and differentiators.
- Price: the price of a product that reflects its perceived value, cost, and market position.
- Place: the place where a product is sold, whether in-store, online or via other sales channels.
- Promotion: strategy used to communicate and promote a product to potential customers.
Ultimately, the “4 Ps” are the foundation of any successful marketing strategy. 😉
Now you know all about pricing strategy examples. See you soon! 👏