Want to learn more about Brand positioning and understand what’s at stake for your company? You’ve come to the right place. 🥳
I’ll walk you through how to define your target market in 4 key steps.
What is the Purpose of Brand Positioning in Marketing?
In a few clear words, marketing positioning is a wonderful brand strategy – it’s the image you have decided to send to consumers when they hear about your brand or your products.
It is defined as the position of your company on the market in relation to the competition and in the eyes of your customers.
It therefore serves to set the tone for your entire marketing strategy, which must be aligned with this positioning. I’ll give you an example that will help you better understand this term. 👇
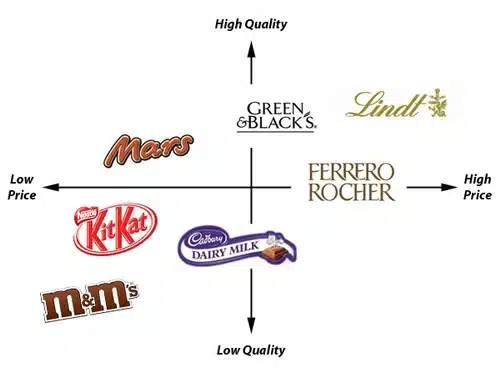
Example of Marketing Brand Positioning: Lindt
Lindt has a marketing positioning based on premium quality. As far as its products are concerned, Lindt positions itself on innovative and elaborate recipes, advocating the greediness of its original creations. The brand even launches the “Lindt’s workshop” range, with new original creations proposed by pastry chefs.
In the minds of consumers, the product is expensive but worth the price because the quality is no longer questionable.
All of Lindt’s marketing revolves around this perception and value proposition. 🍫
Introduction to Brand Positioning Strategy
I’ll now go into detail about how to achieve such marketing precision and why it’s so important. Then I’ll show you how to do a “positioning mapping” against the competition and give you two more examples to really understand how positioning works. 🤓
The Importance of Marketing in Brand Positioning
Positioning serves many business purposes and can be a key driver of your digital marketing strategy and brand identity. 🔑
💡 The benefits of clearly defined marketing positioning are :
- Establish your position on the market and à identify the target customer most likely of to convert.
- Maintain a consistent approach to marketing by following a clear editorial line.
- Explain your pricing for all products based on your target audience and your brand image in the marketplace. (Like Lindt)
- Foster empathy with existing and potential customers, increasing the chances of customer loyalty: your brand is recognized and appreciated for its value
- Focus marketing on a single audience and combine the most effective marketing tactics.
- Create a better environment for analyzing the success of strategies and repurposing them.
The Impact of Brand Positioning on Your Prospects and Customers
Today‘s consumers are very concerned about what‘s behind the products they buy, the image that the brand sends back to them is increasingly important for new generations of buyers.
Nevertheless, they also want more and more speed in obtaining goods and therefore in their purchasing decisions. They make quick decisions based on the company’s business strategy and market positioning.
💡 From the customer‘s perspective, effective positioning is therefore very important for many reasons.
- The customer adapts his budget according to the brands: he knows where to find expensive and qualitative products, he knows where to find discount brands, and understands the pricing…
- He will also be able to make his consumption choices in a wider way and know in which supermarkets he will find the right products for his needs,
- He will be able to choose brands according to the values they advocate: environment, animal welfare, and flavors…
- In a global way, his consumption choices will be validated.
A clear picture of your brand‘s strategic positioning saves you time and helps you make decisions faster.
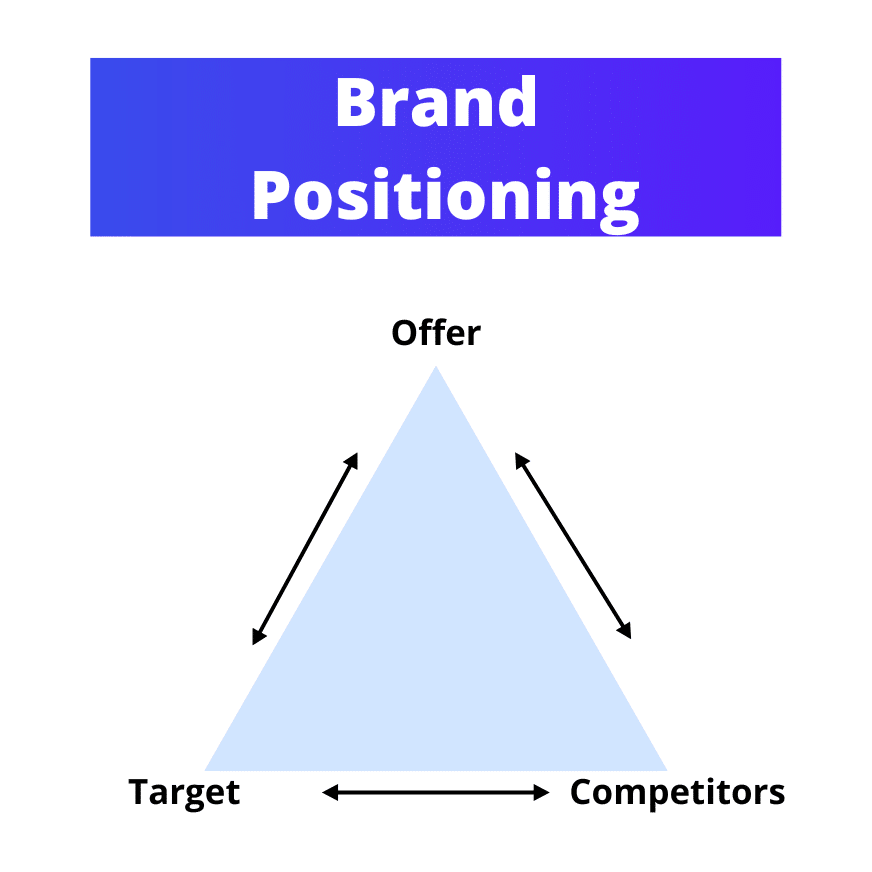
The Golden Triangle of Brand Positioning
In order to better understand the stakes of brand positioning, you need to know that it is composed of 3 actors that we call together “the golden triangle of positioning”, these are the 3 factors that must absolutely be taken into account when creating the strategy.
1. The Offer
What exactly are you going to sell? What are the advantages and limitations of the product/service?
2. The Target
Who are you going to sell it to? Have you done your targeting and segmentation? What do your potential customers look like, and what are their consumption habits?
3. The Competition
Have you done a market study? Who is already in the same market as you, and what are their offers? What do their offers have that you don’t?
How to Define Brand Positioning in 4 Steps?
Well, now that you understand all the issues of a good marketing positioning, we can move on to the heart of the matter: how to create your positioning and keep this line of action in a complete marketing strategy? 😍
1) Understand Your Market
The first thing to do is to understand the target market, understand how it works in a global way.
What type of market are you in?
Consumer Products Market
The consumer products market has a large number of offerings: clothing, personal care products, household products, furniture, household electronics, food, toys, most everyday items.
It is the largest of all markets and is generally very competitive.
- On the French market, with the laws in force in the country.
- In the consumer products market.
- On the food market and more specifically chocolate.
Financial Markets or Investment Products
Financial markets are places, physical or virtual, where market participants meet to trade financial products:
- The capital securities,
- Investment shares,
- Debt securities.
- On the European market,
- On the financial market,
- On the banking market and more specifically the interest rate market.
🏫 Each market is made up of its own rules that must be known and understood. A bank’s positioning can be focused on “security” “ease” or “price competitiveness”, depending on its objective, its clientele, and its offer. This is why defining its positioning is essential.
Industrial Products Market
The industrial market is quite vast. It is composed of a large number of tools or machines, and each company can position its offer differently. Its specificity is to be focused only on industrial customers and therefore companies. The actors of this market will not market to individuals.
Here are some examples of what is sold in the industrial sector: Air compression machines, industrial vehicle parts, torpedoes for submarines, maintenance products for machines.
- You are on the European, American, and South American markets… and each of these markets has its specificity that you need to know.
- You are in the industrial products market,
- You are on the naval market and more precisely on the boat parts market.
Services Market
The services markets have for objective the realization of services. Their goal is not to sell you a product, but rather a service. It is possible to sell services to a company or a household:
- A beauty salon sells services to consumers.
- A recruitment company sells services to businesses.
- You are in the Paris market,
- You are in the B2B (business to business) market,
- You are in the services market,
- You are on the event market
Understanding the Market in a Holistic Way
I hope that understanding the market is easier for you. If you want to understand even more about the market issues in the country where you are located, you can use the PESTEL analysis.
Use PESTEL Analysis
It looks like this. 👇 And it gives you a better understanding of the limitations, and threats but also the advantages of the market you are positioned in.
2) Understand Your Target
In all good positioning strategies, you need to create target segments. Once you have identified which market you are positioned in, you need to look in more detail at the consumers of that market. That is, the “target” of your marketing. 🎯
In marketing, there are several targets: The primary target, the core target, and the secondary or relay targets.
Defining the Primary Target
The primary target is your buyer persona in the broadest sense of the term.
Primary target: That is, all the customers to whom the brand or company hopes to sell its product or service.
Let’s take a look at some concrete examples to better understand who you are going to target.
Example 1:
- 🤓 You have a hair salon for women located in Paris.
- 🎯 Your main target will be “women between 18 and +65 years old in Paris”.
Example 2:
- 🤓 You sell French management software to digital companies.
- 🎯 Your main target will be “Digital companies based in France”.
Defining the Core Target
The core target is the target that is most likely to buy your product. That is to say, an even finer and more exact fragment than your main target.
It is important to define the core target of your brand or product because you will focus all your marketing strategies around the core target. These are the people you will talk to first.
To create the best possible core target, you should think about building a “marketing persona” file.
That is to say, define a maximum of criteria that will help you determine who your core target is and how to talk to them. Among these criteria, you can find :
- ✔ How old is it?
- ✔ What is his professional situation?
- ✔ What are his means of communication?
- ✔ To which generation does she belong?
Once all your criteria are noted on a persona sheet, you will be able to move forward on your offer – be able to better understand, define and communicate it. 😁
Define the Relay Targets
The last type of target to identify is the relay target. They are not directly interested in your offer, but they can be very good communication levers: they can be influencers, journalists, and more and more influencers.
Influencers and brand influencers are more and more used to reach your core target. You can already start looking at who could talk about your products to your targets.
❤ The question to ask: Which influencers are likely to talk about my product to my target in this market?
Understanding your targets will help you identify your type of positioning. But, it is not possible to know the target, without knowing everything about the offer.
3) Understand Your Offer
Understanding your offer also means understanding your products and where they fit in the market of goods and services you are targeting.
You need to make sure you understand your product and its competitive advantages.
- ✔ What are the features/options?
- ✔ How will my product/service differentiate and stand out?
There are several types of “marketing positioning” to differentiate your product in the market, if you haven’t already thought about this type of information, I’ll give you some pointers to better understand where you can position yourself. 🤓
1. Positioning on Benefits
In the early days of your strategies from positioning marketing, the brand focuses on the specifics of the product or service. That is, you offer something that competitors do not.
Do the features of your product make a difference? Here are two examples:
Example 1:
- 🚀 You sell B2b prospecting software: the difference between your software and the competition is that you offer custom services to tailor the tool to each client. This means that you position yourself on the advantages to differentiate yourself from the competition.
Example 2:
- 🚉 You are a travel company, and you sell all-inclusive offers, you have a 24-hour support service. So, you focus on the offers and their benefits rather than the prices.
2. Positioning on Quality
Here, the brand focuses on its style and luxury. In this second marketing positioning strategy, consumers pay a higher price for the quality of the product or for the brand image.
Example 1:
🩳 Abercombie sells its products at a higher price, but the brand has a strong value proposition: Lacoste’s “luxury” positioning allows it to sell its products at a higher price.
Example 2:
🍵 You want to open a tea shop, all your products are organic and local. So you are going to bet your marketing communication on the quality of the products to show the difference between your salon and the competing salons. You will propose elaborated recipes and bet on the user experience, the products will be good and fresh and will justify the high prices.
3. Price Positioning
In this example of positioning, the brand asserts itself by offering a product that offers the same benefits as its competitors but at a reduced price. Price positioning always means that the price is cheaper than the competition. There are several “low-cost” brands whose main target is middle-class or working-class households. The goal is to sell quality products at low prices.
Examples:
🏪 Big box brands like ALDI or LIDL that offer a whole range of very cheap products.
💻 Some e-commerce sites are specialized in low prices, like AliExpress.
4. Positioning on Options
The fourth and final example of brand positioning is through differentiation through options. The objective here is to market a specific feature or use of the product. Can be used in certain situations. This is slightly different from positioning on benefits. Here we are talking about a product with additional options.
Example:
🥽 You sell glasses, and each person who enters your store has a wide choice of frames, styles, colors, and pricing. Your store will therefore focus its communication on the fact that “everyone can find their pair of glasses” since you have a lot of options.
4) Positioning Map
Competitive positioning mapping is a marketing tool that has been used for many years in business school. 🎒
It is used to place the product or brand against the competition in the same industry to see at a glance what the brand’s value proposition is and how to make it stand out in the market.
Although today it is presented as an academic tool, it is still widely used in marketing agencies and allows the development of a marketing strategy.
The first things to do when you decide to do a mapping are:
- ✔ Identify 2 important criteria for your brand that you want to emphasize in your marketing strategy.
- ✔ Choose a handful of heterogeneous competitors (it’s impossible to be able to score the entire competitive list).
Next, I’ll show you concretely what it looks like. 👇
Examples of Brand Positioning
Abercombie & Fitch’s : Brand Positioning
The Abercombie & Fitch brand decided to position itself on “quality”, the prices are higher and the products are premium.
The two points on which the brand wants to engage are:
- 👐 Customer experience: The customer is at the center of the brand, the goal being that they feel privileged and accompanied during the purchase.
- 😎 The strong identity of the brand / its American identity: Abercombie’s goal is to be recognized as a powerful American brand, a guarantee of beauty and success.
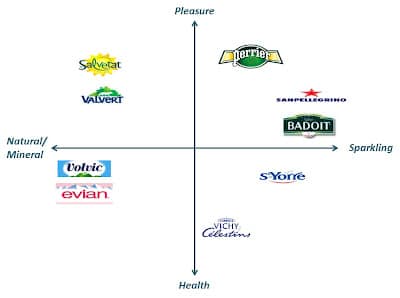
Evian : Brand Positioning
💦 The Evian brand is positioned on well-being and nature. Prices are more expensive than some competing brands like Cristaline and Contrex, but Evian differentiates itself through its value proposition: quality water that keeps you young and healthy.
Conclusion of Brand Positioning
To conclude, you need to identify 3 important factors to define your brand positioning: your offer, your target, and your competition.
To do this, follow the steps of this article and define, step by step, all the criteria for the positioning of your company or your products.
Now you know everything about brand positioning, you can start answering the questions to create yours without making mistakes:
- Who is my target audience,
- What are the details of my product,
- What market am I in and who are my competitors.
FAQ of the Article
What is Product Positioning?
Marketing positioning is not always the same for all the products of a brand. Each product will have a different way of being identified on the market, two products of the same brand can also have completely different targets:
Take for example the visual identity of Lacoste 🐊, some of their luxury products are aimed at wealthy targets, interested in the latest trends. Other items like tracksuits and “classic” caps are going to be thought for the middle class. The brand has managed to adapt to its buyers and diversify the targets according to the models.
You can easily see the same thing on car brands that offer different models, from standard to premium.
Positioning helps you to build an emotional connection with the customer.
How to Test Your Brand Positioning?
In order to test the marketing positioning, you can use the Kapferer identity prism. This technique allows you to know which emotions the future customer goes through when he is interested in the brand and buys the product. That is to say, if they feel valued, belonging to a certain community, or if, on the contrary, they are very detached from the brand and are only interested in the price, for example.
Successfully identifying the user experience allows you to test the global brand positioning.
Moreover, you can check who buys your products and if they really correspond to the target you had identified.
Once the product positioning is in place, you can launch marketing, communication, and sales actions.
There you go, now you know how to manage your brand positioning effectively! ⚡