Cross selling. I first came across this word when ordering a pizza 🍕
Just before paying, a pop-up offered me “A drink for 2€ more?”.
As I was thirsty, I clicked. 🧋
This wasn’t just another sale, it was cross-selling: offering a complementary product at the right time.
Okay, so this is a B2C example, but it’s the same principle in B2B.
Selling prospecting software? You can offer CRM.
Selling an HR management tool? You can offer a payroll solution.
As you can see, today we’re going to look at how to apply this strategy. 😇
All without pizza pop-ups, I promise. 👀 (Reading time: 3 minutes).
What is cross selling ?
Cross-selling involves offering a customer a product or service that complements their main purchase. Let’s take a simple example. ⬇️
A customer subscribes to your sales prospecting offer. In addition, you offer them an advanced reporting module, CRM integration and personalized support.
Additional services don’t replace the basic offering, but complement it in a relevant way.
The aim of cross-selling is twofold:
- 1️⃣ Increase the average basket, without lengthening the sales cycle too much.
- 2️⃣ Increase customer satisfaction, by meeting specific needs.
It also enhances the value of your expertise. 👀
What are the advantages and disadvantages of cross selling?
Now that you know what it is, it’s important to understand the pros and cons of the cross-selling strategy. 👇🏼
| ✅ Positive points of selling cross | ❌ Negative points of selling cross |
|---|---|
| Increased sales: the average basket increases without further prospecting. | Risk of over-solicitation: too many suggestions can damage the customer experience. |
| Greater profitability: selling to an existing customer costs less than acquiring one. | Mandatory relevance: a bad recommendation can discredit your offer. |
| Strengthened customer relationship: you show that you understand their real needs. | Offer complexity: adding options can make the decision to buy more difficult. |
| Medium-term upsell opportunities : a better-equipped customer becomes more commercially mature. | Internal resource requirements: marketing, sales and product must be well coordinated. |
| Increased loyalty: a well-supported customer is more likely to renew. | Sometimes difficult to measure : it can be difficult to isolate the direct impact of cross-selling. |
Differences between cross-selling and upselling
Cross-selling and upselling are two complementary sales techniques with different objectives.
1️⃣ Upselling: selling a higher-end product.
The aim of this technique is to move the customer towards a more advanced or more expensive version of the offer they were initially considering.
The aim is to increase the value of the contract by offering more features.
Example: your prospect is interested in the basic license of your SaaS tool. You present him with the “Pro” version, which includes advanced automation, more users and premium support.
2️⃣ Cross selling: selling complementary products.
The aim is to offer a product or service that complements the main purchase. It does not replace what the customer has chosen, but rather accompanies it.
The aim is to meet a related need or optimize the use of the initial product.
Example: you sell prospecting software. In addition, you offer a training service for sales teams, or integration with a CRM.
B2B example: you sell prospecting software. You also offer a training service for sales teams, or integration with a CRM.
And if you’re still not quite sure, here’s a table that explains when to use one or the other. ⤵️
| Criteria | Cross selling | Upselling |
|---|---|---|
| Type of offer. | Complementary product/service. | More complete or high-end product/service (different of high ticket sales) |
| Time in the sales cycle. | During or after purchase. | Before or during purchase decision. |
| Objective. | Optimize use of initial product. | Maximize contract value. |
| B2B example. | Training, support, third-party integration. | Upgrade from “Basic” to “Premium”. |
How to succeed in cross-selling?
Implementing this kind of strategy means knowing your offers, your customers and, above all, implementing the right actions at the right time.
That’s why here are 5 essential steps not to be missed. 👇🏼
1) Study the offer and identify complementary products
First and foremost, you need to take stock of your catalog. 🛍️
Which products or services can really complement each other?
The aim here is not to increase the basket at all costs, but to improve the overall customer experience. 💌
To achieve this, you can:
- 🥇 Analyze your sales history ⭢ which products are often bought together?
- 🥈 Involve your sales and Customer Success teams ⭢ they’re the ones who know the needs.
- 🥉 Group your products or services by functional universe ⭢ for example, prospecting + follow-up + reporting.
Example: if you sell a prospecting tool like Waalaxy, you can add a complement like adding an integrated CRM module. 👽
2) Segment your customers
Offering the right product to the wrong target wastes time and credibility.
The key 🔑 to a good cross-selling strategy lies in personalization.
To achieve this, you need to segment your customers according to certain criteria:
- Company size (VSE, SME, ETI, etc.).
- Business sector.
- Job title.
- Purchase history.
- Product use.
This segmentation enables you to create targeted, high-value offers.
For example, a customer who already uses 80% of your tool’s features might be interested in an “advanced” version. 👀
However, avoid sending a blanket recommendation to your entire base. This will completely discredit your expertise. ❌
3) Implement the strategy
Now it’s time for action. This means intelligently integrating your strategy into your existing contact points:
- In app (in your SaaS tool) ⭢ offer an add-on module just when the user needs it. On Waalaxy, you can redeem additional credits if you’ve used it all up.
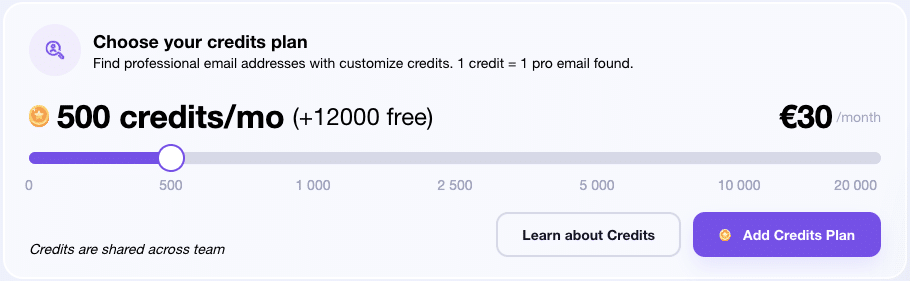
- Payment modal ⭢ just before validation, propose a strategic addition (ex: Add this feature for €20 more).
- Sales appointment ⭢ propose a sales appointment to unblock a situation or talk pricing.

And if you want to be at the top of your game, you can :
- Think timing: the right product, at the right time.
- Test different locations and formulations to find what works best.
- Use social proof: import Google reviews into your landing page.
4) Create post-purchase automation scenarios
Cross-selling doesn’t stop with the purchase. It starts after the sale.
A satisfied customer is more likely to accept a complementary offer if he feels it meets a real need.
To achieve this, you can :
- 🔵 Automated emails: sent a few days after purchase with a complementary product. Example, “now that you’re using [product], here’s how to go further”.
- 🔵 LinkedIn messages or CRM sequences: sent a personalized message by the sales person following the customer, with advice on how to use the product.
- 🔵 Useful content: offer a guide, comparison or webinar that talks about the additional functionality.
5) Measure results
Last but not least, it’s time to analyze the results. 🔍
It’s essential to track the right indicators to know what’s working and what needs adjusting.
To that end, we’ve put together 🍜 a short list of KPIs to keep an eye on:
- Cart addition rate.
- Complementary product adoption rate.
- Cross sell conversion rate by channel.
- Increase in average customer basket or customer value (CLV).
- Churn rate of cross-selling customers.
- Overall ROI of your actions.
How about a recap?
Cross-selling isn’t just another aggressive sales technique or marketing trick.
It’s a real strategic lever based on understanding your customers, their objectives and what can really make their lives easier.
Here, we’re not talking about selling more to sell more, but selling better. 👀
But for this to work, you need concrete preparation:
- Good segmentation.
- Good information flow between marketing, sales and product.
- A real desire to provide value above all else.
So if you’ve got the right products and the right tools, there’s only one thing left to do: take action. 🔥
What’s cross-selling?
Cross-selling is a service or product that complements a purchase, with the aim of creating more value for you and your customer.
What’s the difference between add-on selling and cross-selling?
They’re not quite the same thing:
- 🔵 Complementary selling (cross selling): consists in adding a product or service that enhances the initial purchase, without replacing it.
- 🔵 Additional selling: broader term used to add any type of item to the initial order, whether it’s a superior product, a service or an accessory.
What are the 3 types of sale?
As part of a comprehensive sales strategy (especially in B2B), it’s important to master the three main types of sales. 👇🏼
1️⃣ Direct sales.
This involves responding to an explicit request. The customer identifies a need, and you propose an appropriate solution.
2️⃣ Upselling.
This involves encouraging the customer to opt for the more advanced or complete version of your solution.
3️⃣ Cross-selling.
This involves adding a complementary product or service to the main offering.
You know all about cross selling. 💸