Have you always wondered 🤔 how the markup rate is calculated? Well, that’s good timing, because our article is going to answer all your questions. Go ahead 👇!
In this article, we’re going to find out :
- ✒️ The definition of mark up rate.
- ☢️ Why it is so important.
- ➕ The calculation.
- ❌ The differences between mark-up and margin rate.
What is the markup rate ?
The brand rate is a key performance indicator that measures the percentage of sales 💰 made in relation to the number of qualified leads. It is a valuable tool for businesses because it will enable you to monitor the effectiveness of your marketing and sales efforts.
It represents the percentage difference between the selling price of a product or service and its cost price. In other words, it’s the gross margin generated by each unit sold. As you can imagine, this rate is of vital importance in a commercial strategy. It enables companies to determine the profit margin 📈 they make on their sales.
A high mark-up rate may indicate a company’s greater capacity to generate profits. If not, you may need to re-evaluate costs or sales prices.
Calculating the brand rate helps you make the right decisions about pricing 🤑 operational efficiency and future investment. By understanding this, you can optimise your profitability and strengthen your competitive position in the market.
The importance of markup rate for your business
As we told you a little earlier, this term is important for several key reasons within your business and financial strategy. Firstly, so that you can keep it straight in your head: it’s an essential indicator of profitability. By calculating the difference between the selling price and the cost price, the brand rate enables you to assess the gross profit margin generated by each sale.
It also plays a crucial role 🎞️ in pricing decisions. A thorough understanding 🧠 of this rate makes it possible to determine competitive selling prices while preserving an adequate profit margin. This can influence customers’ perception of the value of the products or services on offer.
This rate also provides valuable information on operational efficiency. A drop in the mark rate can signal problems… These could include high production costs or increased competition. By regularly monitoring this rate, companies can identify opportunities to optimise costs and streamline operations.
In addition, the mark rate influences investment and growth decisions. Investors and lenders often look at this ratio to assess a company’s financial strength and ability to generate long-term profits.
As you can see, it is a vital ⚒️ tool for assessing financial health, guiding pricing, optimising operations and making informed investment decisions, all of which contribute to a company’s success and sustainability in the competitive marketplace.
Calculate markup rate
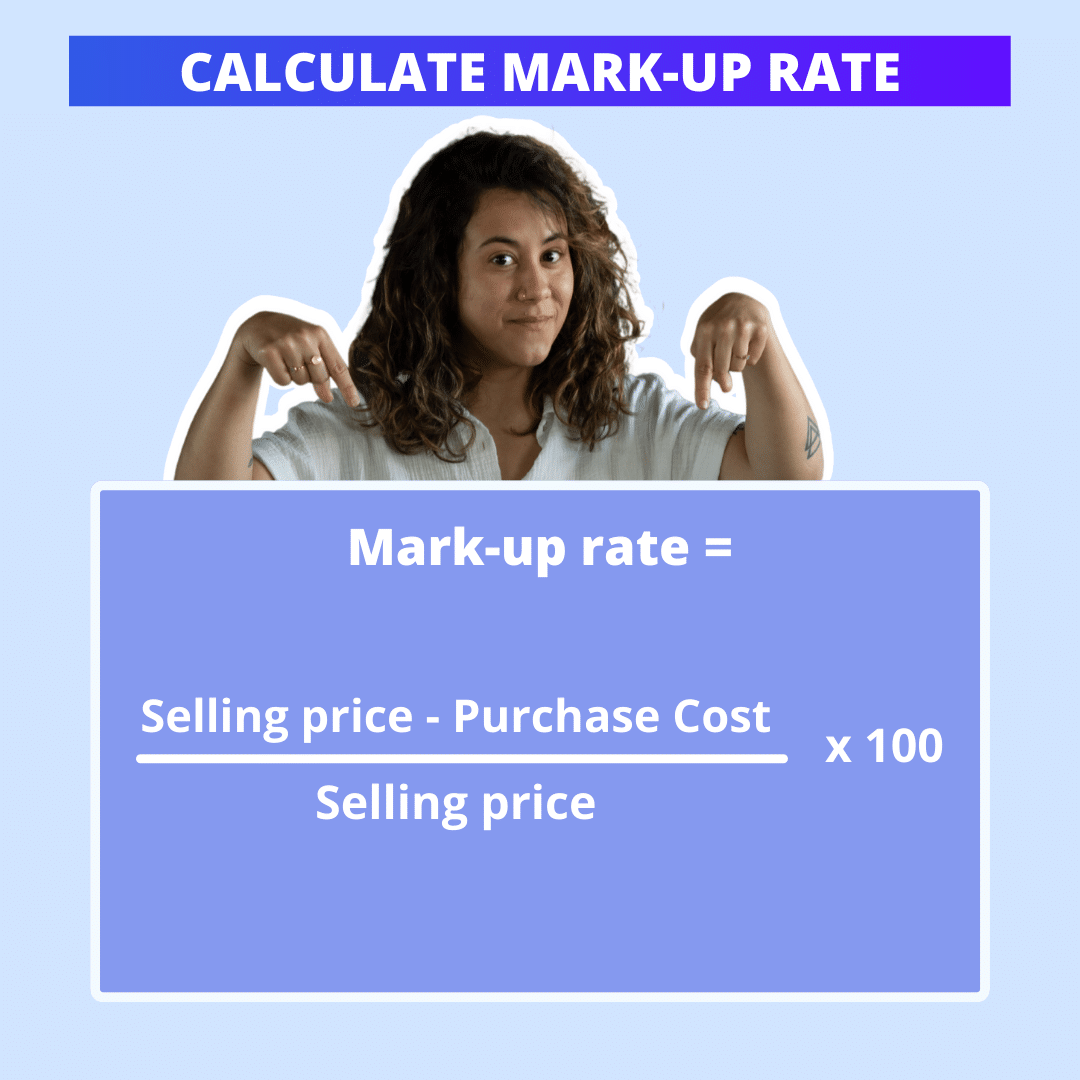
You may be waiting for it, but we’re going to move on to calculating the markup rate 🤩. Rest assured, there’s absolutely nothing complicated about it. It’s relatively simple and here’s the formula to use to find out how to calculate it 👇:
Markup rate = ((Selling price – Purchase cost) / Selling price) x 100
Where :
- The selling price is the amount for which you sell a product or service.
- The purchase cost is the total cost of acquiring or manufacturing the product, including direct and indirect costs.
Once you’ve made the calculation, multiply the result by 100 to obtain the percentage mark-up.
For example, if you sell a product for €150 and its purchase cost is €100, the mark up rate calculation would be as follows:
Markup rate = ((150-100)/150) x 100 = 33.33%
This would mean that your mark-up rate for this product is approximately 33.33%. This indicates the gross profit margin achieved on each sale 💰.
How can you improve your brand rate?
Do you already know your brand rate but want to improve it? To improve your mark-up rate and increase your company’s profitability, here are some strategies to consider:
- ➡️ Cost optimisation: Identify 👀 areas where you can reduce production, supply or operating costs without compromising quality.
- ➡️ Negotiating with suppliers: Try to negotiate better rates with your suppliers or explore new sources of supply.
- ➡️ Efficient stock management: Avoid overstocking and stock-outs to minimise storage costs and maximise stock rotation.
- ➡️ Product enhancement: Improve customer perception 💞 of the value of your products or services through strong marketing and positioning.
- ➡️ Offer diversification: Offer complementary products or services to increase your customers’ average shopping basket.
- ➡️ Product innovation: Develop new features or premium versions of your products to justify higher prices.
- ➡️ Customer segmentation: Identify customer segments prepared to pay a higher price for specific benefits and adapt your offer accordingly.
- ➡️ Improving the customer experience: Offer excellent customer service 🍸 fast delivery and customisation options to justify higher prices.
- ➡️ Process automation: Use technology to automate repetitive tasks and reduce operational costs.
- ➡️ Ongoing evaluation and adjustments: Regularly monitor your brand rate, analyse performance and make any necessary adjustments to your sales strategy.
It’s important to note that improving brand rate requires a balanced approach. Assessing the opportunities and risks associated with each strategy and adjusting accordingly can help to achieve sustainable results.
What is the difference between markup rate and margin rate?
Before we look at the differences, it’s a good idea to understand the definition of margin.
The mark-up is a percentage that indicates how much a company earns on each euro it sells. It is calculated by dividing gross margin by sales. Gross margin is the amount of money earned after deducting the cost of goods sold. Turnover is the total amount earned from sales.
This margin rate is an important indicator of a company’s financial health. A high margin rate indicates that the company is in a position to generate significant profits on its sales. A low margin rate indicates that the company is struggling to cover its costs.

So, you see, both rates are financial measures used to assess a company’s profitability. You can use both.
The brand rate only takes into account the cost of goods sold, while the mark-up rate takes into account all costs.
Calculating the margin rate
The formula for calculating the mark-up is as follows:
Margin rate = Gross margin / Sales
For example:
You sell goods for a total of €100,000. The cost of goods sold is €50,000. The gross margin is €50,000. If sales are €100,000, the margin rate is 50%.
In general, a higher mark-up rate is preferable to a higher margin rate 👍🏼. This is because a high brand rate indicates that the company is able to generate a higher profit on each product sold.
However, it is important to note 🖊️ that a higher margin rate may be preferable to a higher brand rate in some industries. For example, companies in the technology industry tend to have higher mark-ups than companies in the manufacturing industry. This is because technology companies can charge higher prices for their products and services. They also tend to have lower manufacturing costs.
Conclusion of the article
All good things must come to an end. But that’s all until the next article. In the meantime, here’s what we’ve seen in the course of this article:
- ✒️ The definition of brand rate.
- Why it’s so important.
- The calculation.
- ❌ The differences between mark-up and brand rate.
Article FAQ
As usual, you know we’re not letting you off the hook until we’ve given you a little insight around our theme. So here’s what we’ve got for you 👇. Because we’re really nice 😉.
What is the ideal margin?
Firstly, the margin is the difference between the selling price of a good or service and the cost of producing or purchasing it. It is expressed as a percentage or in euros. Margin rates can vary from one industry to another. As such, there is no ideal margin to achieve 💘.
Of course, you should bear in mind that if your margin rate is high, then the company is in a position to generate profits on its sales.
How do you calculate a selling price from the mark-up rate?
To calculate 🤓 a selling price from the brand rate, you can use the following formula:
Selling price = Cost + (brand rate x Cost)
Here, your cost is the purchase cost (of goods) of the product and your brand rate is the percentage of profit you want to make on the product. Remember, however, that your selling price must be expressed in euros.
And that’s it, you now know how to calculate the markup rate to improve all your strategies.